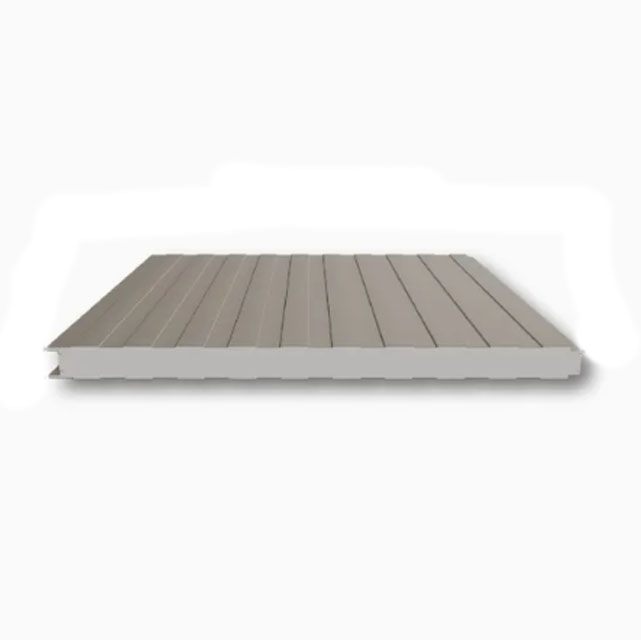
Sandwich Building Panels
Lightweight and High Strength:Made from a combination of different materials, formed by rolling and high-pressure bonding, resulting in a solid, lightweight, energy-efficient building material.
Superior Performance:Interlocking cavity design offers fire, moisture, heat, and sound insulation, meeting building needs.
Aesthetic Appeal:Various styles, from modern to classic, offering outstanding architectural effects and strong visual impact.
Easy Installation:Large panels with plug-in installation, factory prefabricated, quick construction, and high installation quality.
Product Introduction
With green building trends rising, Sandwich Building Panels are key innovations. Addressing traditional structures' limitations, they use metal-polyurethane for load-bearing, combining high-performance PV modules for insulation and solar power conversion. Modular design simplifies construction/maintenance, while waterproof/fireproof features enhance durability. A versatile sustainable solution for modern green architecture.
Characteristics
Details of BeautFacade System
The BeaufFacade System features high-quality components designed for durability and performance. It includes a Parapat Cap for seamless integration, Purin elements for enhanced functionality, and the HXY-FD-W-LH18 module for structural stability. The system is completed with a Bottom Flashing to ensure weather resistance and long-term protection. Ideal for modern architectural projects, this system combines innovation with reliability for superior facade solutions.
Color Selection
Discover a vibrant array of steel sheet colors! From the subtle sophistication of ivory and beige to the lively charm of emerald green and lime, and the striking appeal of raspberry and hot pink, our diverse color palette caters to every aesthetic taste. With a wide selection of both classic and unique hues, we make it easy for you to find the ideal color that perfectly matches your design ideas and project requirements.
Certifications
Our company is certified with CE, ISO 9001, SGS, and FM, ensuring compliance with EU standards, robust quality management, strict testing protocols, and fire safety requirements. These accreditations demonstrate our dedication to excellence, reliability, and leadership in the industry.
Sandwich building panels are a core element of modern construction, offering superior thermal insulation, structural integrity, and rapid installation. These panels, also referred to as insulated metal panels (IMPs) or composite panels, consist of a core insulating material bonded between two rigid facings. Their ability to meet rigorous demands for energy efficiency, fire safety, acoustic control, and mechanical strength makes them ideal for commercial, industrial, and residential buildings.
This article provides a comprehensive, technical, and SEO-optimized overview of sandwich building panels, addressing their materials, industry standards, engineering behavior, regulations, and installation practices, along with answers to frequently asked questions and a professional call to action.
What Are Sandwich Building Panels?
A sandwich building panel is a prefabricated composite element made of:
Two outer facings (usually pre-painted galvanized steel, aluminum, or fiber-reinforced plastic).
One core insulation layer, commonly made of polyurethane (PU), polyisocyanurate (PIR), expanded polystyrene (EPS), extruded polystyrene (XPS), or mineral wool (rockwool).
These panels provide thermal insulation, structural strength, and quick modular installation, reducing construction time and long-term energy costs.
Engineering Composition and Core Material Types
1. Outer Facings
Material: Galvanized steel (0.4–0.7 mm), aluminum, stainless steel, or fiber-reinforced plastic.
Coatings: Polyester (PE), PVDF, Plastisol, or polyamide for corrosion resistance and aesthetics.
Role: Structural support, weather protection, and finish layer.
2. Insulating Core Materials
| Core Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Fire Resistance | Density (kg/m³) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PUR | ~0.022 | B2/B3 (DIN 4102) | 30–40 | Cold storage, industrial |
| PIR | ~0.021 | B-s1,d0 (EN 13501-1) | 30–50 | Fire-rated envelopes |
| EPS | ~0.035 | B2 | 12–30 | Cost-effective insulation |
| Rockwool | ~0.040 | A1 (non-combustible) | 80–150 | Fire-resistant walls/roofs |
Key Technical Benefits of Sandwich Panels
High Thermal Efficiency: U-values as low as 0.18 W/m²·K reduce HVAC load.
Fire Resistance: Rockwool and PIR cores can meet EN 13501-1 Class A1 and B-s1,d0.
Quick Installation: Lightweight with tongue-and-groove or concealed fastener systems.
Structural Load Capacity: Can support wind and snow loads per EN 14509.
Moisture & Corrosion Resistance: Protective coatings and core material properties enhance lifespan.
Compliance with Industry Standards and Codes
Sandwich panels must comply with multiple national and international standards:
| Standard/Code | Description |
|---|---|
| EN 14509 | European standard for self-supporting double-skin metal panels |
| EN 13501-1 | Fire classification of construction products |
| ASTM E84 / E119 | US standard for surface burning/fire resistance |
| ISO 9001 / ISO 14001 | Manufacturing and environmental quality standards |
| FM Approved | Panels tested for wind uplift, fire, hail resistance |
| LEED / BREEAM | Eligible for green building certifications |
Applications of Sandwich Building Panels
Sandwich panels are suitable for both load-bearing and non-load-bearing applications:
1. Industrial and Commercial Buildings
Warehouses, factories, logistics hubs
Quick-build offices and workshops
2. Cold Chain and Clean Rooms
Food storage and processing centers
Pharmaceutical and electronic clean environments
3. Public and Residential Infrastructure
Schools, hospitals, sports complexes
Modular housing and container structures
4. Roofing and Facades
Lightweight pitched or flat roof systems
Aesthetic facades with concealed joints
Installation and Safety Considerations
Best Practices for Installation
Panels must be stored horizontally, off the ground, and protected from moisture.
Ensure framing is level and aligned before panel placement.
Use appropriate fasteners and sealing systems (butyl or EPDM gaskets).
Joint sealing and vapor barriers are critical for airtightness and insulation continuity.
Thermal bridges must be avoided by using thermal breaks or properly aligned joints.
Safety and Handling
Use proper PPE for cutting (dust mask, gloves).
Follow fire safety precautions for combustible cores during welding or torching near panels.
Use lifting gear or panel lifters for long panels (>6m) to prevent deformation.
Technical Performance Overview
| Property | Value/Range |
|---|---|
| U-value (thermal transmittance) | 0.18 – 0.45 W/m²·K |
| Sound Insulation (Rw) | 25 – 35 dB depending on core thickness |
| Load-bearing capacity | Up to 3.5 kN/m² (depending on span & support) |
| Fire Resistance (EI) | 30–120 minutes (Rockwool/PIR cores) |
| Panel Length | 2–12 meters |
| Panel Thickness | 40–200 mm |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What’s the difference between PU, PIR, and Rockwool cores?
A: PU and PIR offer superior thermal insulation. PIR has better fire resistance than PU. Rockwool is non-combustible and ideal for applications requiring high fire protection.
Q2: Can sandwich panels be used for load-bearing walls?
A: Yes, many sandwich panels are engineered to support structural loads in accordance with EN 14509. However, project-specific load calculations are essential.
Q3: How do sandwich panels contribute to energy efficiency?
A: With low thermal conductivity, sandwich panels minimize heat transfer, reducing energy use for heating and cooling, especially in climate-controlled buildings.
Q4: Are sandwich panels sustainable?
A: Yes. Many are recyclable, manufactured with low-VOC coatings, and help earn LEED/BREEAM points due to energy-saving and low-carbon properties.
Q5: What maintenance is required?
A: Minimal. Inspect joints, sealants, and coatings annually. Wash panels to maintain aesthetics and performance in corrosive environments.