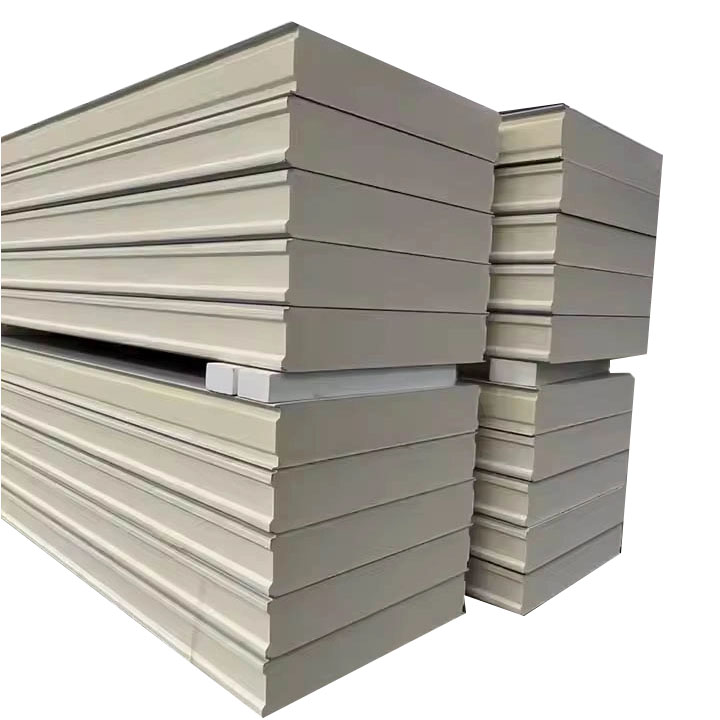
Sandwich Panel PU
Thermal insulation: Ultra-low thermal conductivity, excellent insulation, reduces heat loss and energy use.
Lightweight & high strength: Low density, light, yet high compressive/bending strength; easy to transport/install, bears loads.
Eco-friendly: No harmful substances in production/use; meets eco standards, recyclable.
Economical: Strong long-term energy savings, cuts operating costs, high value.
Corrosion resistance: Good chemical resistance, suits harsh environments, long lifespan.
Product Introduction
Polyurethane sandwich panels are a high-performance building material that consists of two layers of metal panels (usually color-coated steel plates, aluminum plates or stainless steel plates) and a polyurethane foam core in the middle to form a "sandwich" structure. The polyurethane core has excellent thermal insulation properties, and is lightweight, high-strength and fireproof, making it widely used in the construction field. This type of panel not only has good thermal insulation and sound insulation effects, but also has excellent waterproof and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for a variety of harsh environmental conditions.
Product Specifications
Lengths of panels | costmized(≤11.8m due to transport |
Width of panels | 500mm-1120mm |
Thickness of panels | 30/35/40/50/60/70/75/80/90/100mm |
Exterior steel thickness | 0.4-0.8mm |
Interior steel thickness | 0.4-0.6mm |
Recommend coating | PE/HDP/SMP/PVDF |
Surface finish | Emboss/Small Wave/Big Rib/Flat |
Density | 40-45 kg/m³ |
Water absorption for 24 hours | ≤1 |
Thermal conductivity | ≤0.023w/m-k |
Compressive strength | 2200kpa |
Fire proof rate | B1/B2/B3 |
Polyurethane (PU) sandwich panels are widely recognized in the construction industry for their superior thermal insulation, structural integrity, and lightweight composition. Engineered as a composite of metal facings and a rigid PU foam core, these panels are a go-to solution for cold storage, cleanrooms, prefabricated buildings, and industrial enclosures.
This article provides a comprehensive technical overview, including materials, manufacturing methods, standards compliance, application insights, and buyer FAQs—designed to help contractors, developers, and importers make informed decisions.
Table of Contents
What Is a Sandwich Panel PU?
Core Materials and Surface Options
Technical Specifications and Performance Metrics
Manufacturing Process Overview
Industry Standards and Compliance
Applications and Engineering Benefits
Installation Guidelines and Safety Considerations
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Conclusion and Call to Action
1. What Is a Sandwich Panel PU?
A PU sandwich panel is a three-layer construction material consisting of:
External Face: Color-coated steel, stainless steel, or aluminum
Core Layer: Rigid polyurethane (PU) foam insulation
Internal Face: Same or different metal cladding as the external layer
PU foam is a closed-cell, high-density insulation material offering superior R-values, moisture resistance, and compressive strength, making the panel ideal for both thermal and structural roles.
2. Core Materials and Surface Options
| Component | Material | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Outer/Inner Skin | Galvanized steel (PPGI), Aluminum, Stainless steel (0.4–0.7mm) | Structural strength, corrosion resistance |
| Core | Rigid polyurethane foam (PUR or PIR) | Thermal insulation, rigidity |
| Coating Options | Polyester, PVDF, Plastisol | Enhanced weather and UV resistance |
PUR (Polyurethane): Lower cost, R-value ~0.022–0.024 W/m·K
PIR (Polyisocyanurate): Higher fire resistance, slightly better R-value (~0.020–0.023 W/m·K)
3. Technical Specifications and Performance Metrics
| Property | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Panel Thickness | 40mm, 50mm, 75mm, 100mm, 150mm |
| PU Foam Density | 38–42 kg/m³ |
| Thermal Conductivity | ≤0.022 W/m·K |
| Fire Classification | B2 or B1 (DIN 4102); PIR can achieve B-s1,d0 (EN 13501-1) |
| Water Absorption | <2% (closed-cell foam) |
| Compressive Strength | ≥150 kPa |
| Sound Insulation | 20–25 dB |
| Panel Width | Standard: 950mm / 1000mm / 1200mm |
| Length | Customizable (≤12m for shipping) |
Cam-lock or tongue & groove edge connections
Enhanced airtightness and structural locking strength
4. Manufacturing Process Overview
1. Material Preparation
Galvanized or pre-painted coils are loaded onto decoilers.
2. Forming and Foaming
Panels pass through roll forming machines to create desired profiles.
Simultaneously, PU foam is injected (via high-pressure foaming machines) between metal facings.
3. Curing and Cutting
Cured at ambient or elevated temperatures for 30–60s.
Panels are precision-cut to specified lengths.
4. Quality Control
Panels are tested for:
Dimensional accuracy
Foam density & adhesion
Thermal conductivity
Surface finish and flatness
5. Industry Standards and Compliance
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| EN 14509 | European standard for factory-made metal-faced insulated panels |
| EN 13501-1 | Fire performance classification (e.g., B-s2,d0, B-s1,d0) |
| ISO 9001 / ISO 14001 | Quality and environmental management systems |
| FM Approved / ASTM E84 | US standards for flame spread and smoke development |
| RoHS / REACH | Chemical safety and environmental compliance |
| CE Marking | EU conformity for structural safety and health |
6. Applications and Engineering Benefits
6.1 Common Applications:
Cold storage rooms & refrigerated warehouses
Clean rooms (pharmaceutical, microelectronics)
Industrial cladding & partition walls
Modular homes & prefabricated buildings
Agricultural buildings (livestock enclosures, poultry houses)
6.2 Engineering Advantages:
Superior thermal insulation (up to 40% better than EPS panels)
Quick installation and labor savings
High strength-to-weight ratio
Minimal thermal bridging
Fire resistance (especially with PIR core)
Excellent resistance to mold, mildew, and corrosion
7. Installation Guidelines and Safety Considerations
Substructure Requirements:
Steel frames or reinforced concrete structures
Panels fixed using self-tapping screws and EPDM washers
Sealing and Finishing:
Silicone or PU sealants ensure weatherproof joints
Flashing and trims for corners, edges, and wall-roof transitions
Handling & Storage:
Store panels horizontally on level surfaces
Use lifting slings with edge protectors
Avoid prolonged UV exposure before installation
Safety Note:
Wear gloves and safety gear; foam offcuts may contain MDI particles
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What’s the lifespan of PU sandwich panels?
Typically 25–35 years with proper installation and maintenance.
Q2: Are PU panels fireproof?
Standard PU (PUR) is fire-retardant (B2/B3). PIR foam offers enhanced fire resistance (B-s1,d0). Always request fire certificates.
Q3: Can PU panels be used for roofing?
Yes. Panels with corrugated profiles and appropriate slopes (≥3%) are suitable for roofing applications.
Q4: How do PU panels compare with rock wool panels?
PU: Better thermal insulation, lighter, lower fire rating
Rock wool: Non-combustible, higher fire safety, heavier
Q5: Is PU foam eco-friendly?
PU production uses petrochemicals but panels are energy-efficient and recyclable. Look for zero-CFC and HFC-free foaming agents.
9. Conclusion and Professional Call to Action
PU sandwich panels represent a cost-effective, high-performance solution for modern construction needs. With outstanding thermal performance, structural integrity, and compliance with international standards, they’re the ideal choice for energy-efficient buildings, cold chain infrastructure, and prefab solutions.