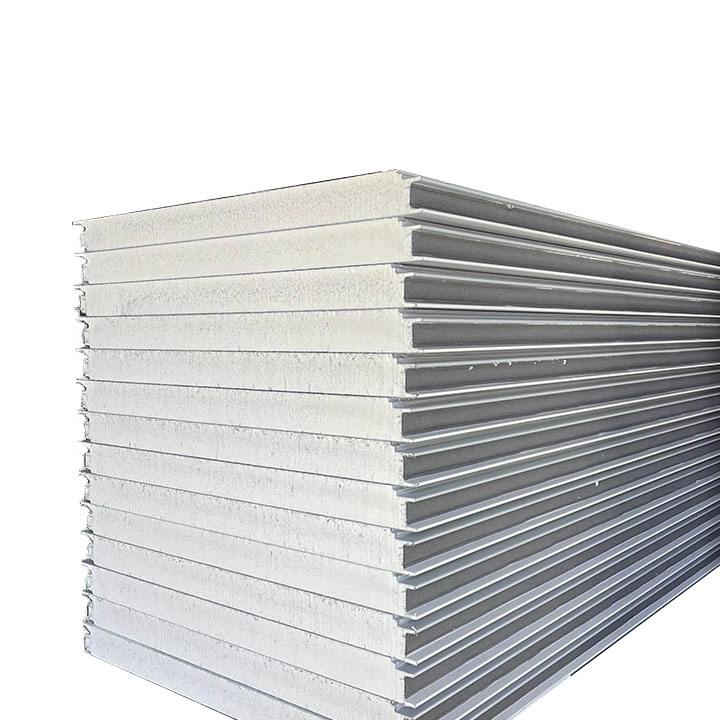
Flat Sandwich Panel
Waterproof: The board structure is tight and has good waterproof performance.
Sound insulation: The porous structure of the EPS core can effectively absorb sound waves.
Energy saving: The thermal insulation performance helps to reduce building energy consumption and achieve energy saving goals.
Economical and practical: The cost is relatively low, the cost-effectiveness is high, and it is suitable for large-scale applications, such as industrial plants, warehouses, cold storage, temporary buildings, etc.
Product Introduction
If you're in pursuit of a trustworthy and environmentally - friendly construction material, EPS sandwich panels are the perfect fit. These panels not only deliver outstanding heat insulation capabilities but also exhibit remarkable fire - resistant properties. By doing so, they guarantee both the safety of the building occupants and a comfortable indoor environment.
Product Specifications
Panel effective width | Roof:950/960mm |
Wall:950/1150mm | |
Steel sheet thickness | 0.40~0.70mm |
Panel thickness | 50/75/100/150/200mm |
EPS density | 12-14kg/m³ |
Color | As per RAL or customized |
Coating | PE,SMP,HDP,PVDF |
Steel type | PPGL,PPGI steel/Aluminum sheet/Stainless steel sheet |
Length limitaion | Max 5.9m for 20FT |
Max 11.9m for 40FT | |
Joint way | Hidden screws type |
Fire proof | B1/B2 |
Advantage | Waterproof |
Resistances of heat-transfer process | 0.035-0.05w/m·k |
Quality Assurance
The company has established a top - tier material testing center laboratory. Outfitted with over 30 pieces of professional equipment, this laboratory is fully committed to two main tasks. Firstly, it conducts comprehensive tests on the physical, mechanical, and combustion properties of raw materials, auxiliary materials, and finished products associated with the enclosure system. Secondly, it plays a pivotal role in the research and development of new products. Moreover, all operations within the laboratory strictly adhere to international - standard operating specifications, ensuring high - quality and reliable results in every aspect of its work.
Flat sandwich panels represent a cornerstone in modern construction and industrial engineering, offering a lightweight, high-strength, and energy-efficient solution for walls, ceilings, partitions, and enclosures. Unlike profiled sandwich panels, flat sandwich panels feature a smooth surface finish on one or both sides, making them ideal for applications demanding aesthetic appeal and precision alignment, such as cleanrooms, modular buildings, and high-spec industrial facilities.
This comprehensive, SEO-optimized article explores the technical composition, performance characteristics, regulatory standards, and best practices related to flat sandwich panels, helping engineers, architects, and procurement specialists make informed decisions.
What is a Flat Sandwich Panel?
A flat sandwich panel is a composite building material consisting of:
Core Material: Insulating medium (e.g., Polyurethane (PU), Polyisocyanurate (PIR), Rock Wool, or Expanded Polystyrene (EPS))
Facings: Smooth steel, aluminum, stainless steel, or high-pressure laminate (HPL)
Adhesive System: Structural polyurethane or phenolic adhesives used under high pressure and heat
Key Characteristics:
Smooth, non-profiled surface (enhanced aesthetics and easy cleaning)
High compressive and shear strength
Excellent thermal and acoustic insulation
Customizable panel thickness and finish options
Technical Specifications and Performance
| Property | Typical Values / Range |
|---|---|
| Thickness | 40 mm – 200 mm |
| Thermal Conductivity (PU/PIR) | 0.018–0.025 W/m·K |
| Fire Resistance (Rock Wool Core) | ≥ 120 minutes (Class A / EI120) |
| Surface Flatness | ≤ ±1 mm/m (ISO 1461 standard) |
| Core Density | PU: 40–45 kg/m³ / Rock Wool: 100–150 kg/m³ |
| Panel Width | 900–1200 mm (customizable) |
| Bending Strength | ≥ 0.5 kN/m² depending on span and thickness |
| Sound Insulation (Rock Wool) | Up to 30–40 dB |
| Water Absorption (EN 1609) | < 2% (PU) / < 1% (PIR) |
Engineering Principles Behind Flat Sandwich Panels
The mechanical and thermal behavior of sandwich panels is derived from composite beam theory, which models the panel as two stiff outer skins resisting bending, with the core material absorbing shear loads. For flat sandwich panels:
Flat facings allow precise edge-to-edge joining, minimizing gaps and thermal bridges.
Symmetric lamination ensures dimensional stability and load balance.
Closed-cell cores (PU/PIR) act as effective vapor barriers.
Rock wool cores provide fire integrity and acoustic damping.
Types of Core Materials and Their Use Cases
| Core Material | Properties | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane (PU) | Excellent insulation, lightweight | Residential & commercial insulation |
| Polyisocyanurate (PIR) | Enhanced fire performance, low thermal conductivity | Cold rooms, cleanrooms |
| Rock Wool (Mineral Wool) | Non-combustible, soundproof | Fire-rated walls, industrial plants |
| Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) | Cost-effective, good insulation | Warehouses, partition panels |
Industry Standards and Regulatory Compliance
Flat sandwich panels must adhere to national and international codes to ensure safety, quality, and environmental performance:
Structural & Material Standards:
EN 14509 – European standard for factory-made sandwich panels
GB/T 23932-2009 – China sandwich panel national standard
ASTM E84 / E119 – US fire performance of building materials
ISO 12572 / 10456 – Thermal and vapor performance
Fire Performance:
EN 13501-1 – Fire classification (e.g., A2-s1,d0 for non-combustible panels)
NFPA 286 – Interior finish material flame spread
Environmental Compliance:
ISO 14001 – Environmental management systems
REACH / RoHS – Chemical and heavy metal safety
LEED / BREEAM – Sustainable building certifications
Common Applications of Flat Sandwich Panels
| Industry / Sector | Application |
|---|---|
| Cleanroom Systems | Walls and ceilings in pharma and electronics |
| Cold Storage | Insulated wall panels with PIR/PU cores |
| Commercial Interiors | Office partitions with sound insulation |
| Data Centers | Non-combustible walls with fireproof cores |
| Modular Construction | Lightweight structural enclosure panels |
| Healthcare Facilities | Easy-clean, antimicrobial surface environments |
Surface Finishing Options
Pre-painted Galvanized Steel (PPGI): Durable and corrosion-resistant
PVDF Coated Steel: Enhanced UV and chemical resistance
HPL / Stainless Steel: Used in sterile and food-grade environments
Antibacterial Coating: For hospitals, laboratories, and food plants
Color and texture customizations are available to align with architectural themes or industry-specific visual compliance.
Installation and Operation Considerations
Panel Handling:
Use lifting equipment with suction pads or foam padding to prevent surface denting
Store in dry, ventilated environments before installation
Installation Tips:
Panels should be mounted on level structural supports
Seal joints using non-hardening polyurethane or silicone sealants
Fix using self-tapping screws with concealed caps or cam-locks (for modular builds)
Maintenance:
Clean regularly using non-abrasive detergents
Inspect sealing lines, joints, and coating for damage or wear
Touch-up paint should match the surface's original RAL code
Environmental & Lifecycle Performance
Flat sandwich panels offer strong sustainability credentials:
Low energy transmission = reduced HVAC load
Long lifespan = 25–40 years with minimal degradation
Recyclable components, especially steel and mineral wool
Contributes to LEED points through thermal insulation and material reuse
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the primary difference between flat and profiled sandwich panels?
A: Flat sandwich panels have smooth surfaces and are typically used for interiors, cleanrooms, or high-spec environments, while profiled panels are more suited for roofing and external walls due to added rigidity and water drainage.
Q2: Can flat sandwich panels be used for structural applications?
A: Yes, depending on core type and panel thickness, they can support structural loads in modular buildings, partitions, and facades. Load-bearing capacity must be verified via span tables and EN 14509 tests.
Q3: What’s the best core material for fire resistance?
A: Rock wool offers the best fire performance, with non-combustible classification (Class A1) and up to 2–4 hours fire rating.
Q4: Are flat sandwich panels suitable for humid environments?
A: Yes, especially when using closed-cell cores like PU/PIR and corrosion-resistant facings (e.g., PVDF-coated steel or stainless steel). Ensure proper sealing of joints to maintain moisture barrier.
Q5: How is airtightness achieved in flat panel installations?
A: Precision-machined edges, cam-lock systems, and sealing gaskets help create airtight enclosures, especially in cleanrooms and controlled environments.